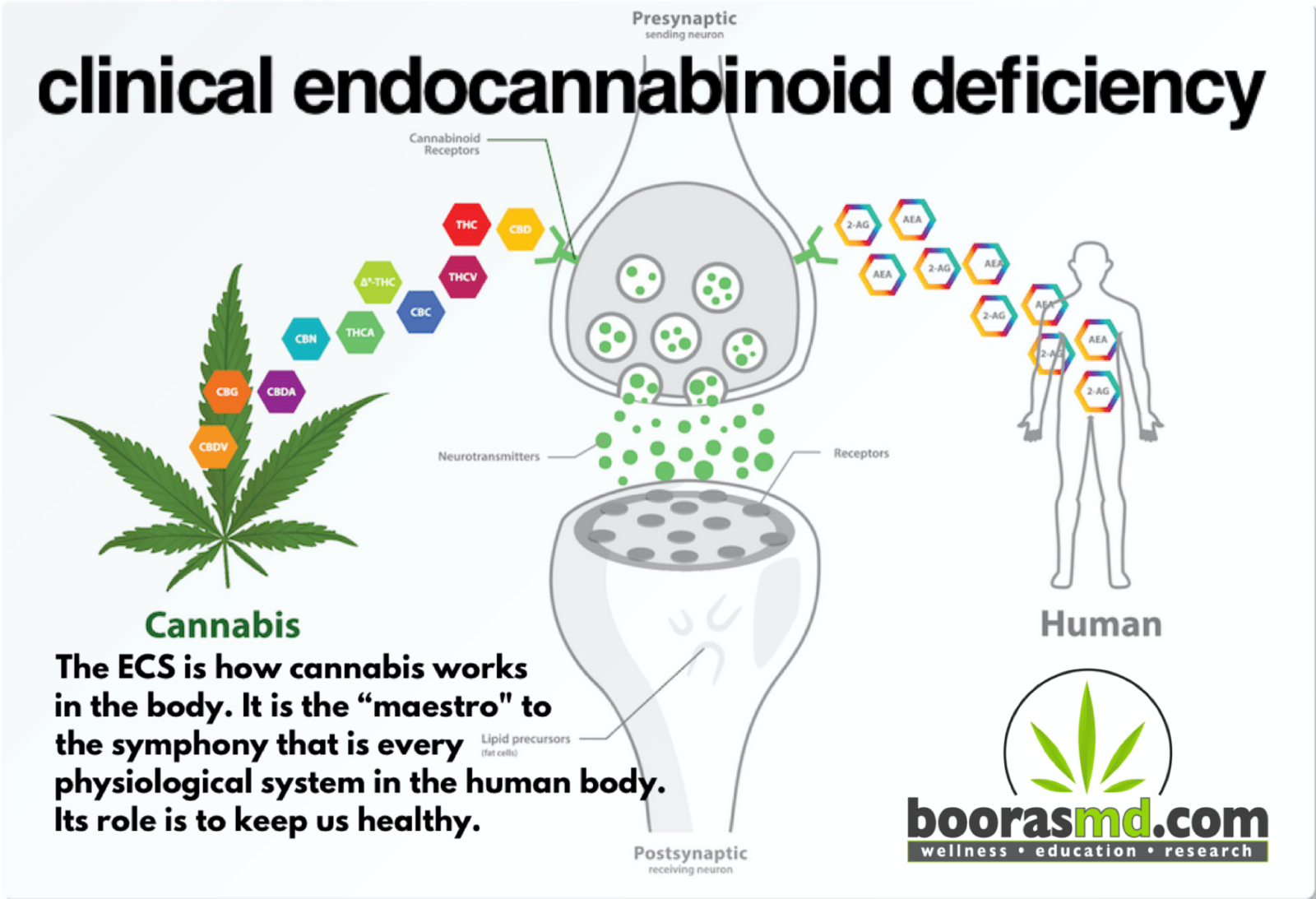
Clinical Endocannabinoid Deficiency
Clinical Endocannabinoid Deficiency Syndrome
In summary, many health problems occur when our body is no longer able to produce enough of its own Cannabis-like compounds (Endocannabinoids). Fortunately, the cannabis plant contains a wide variety of over 130 cannabinoids and other natural substances, like terpenes, that are able to activate the Endocannabinoid System (ECS) in these deficiency states (see the list below). When the ECS is activated our body is able to activate very complex and powerful systems of self-repair and prevention.
Physiologically, our bodies are able to maintain internal balance (homeostasis). The most widespread regulatory physiologic system in the body is the Endocannabinoid System. Scientifically, cannabis experts think of the ECS as a vital cellular signaling system that is responsible for regulating a person’s pain, appetite, mood, memory, and cellular life and death cycles.
The ECS is the “maestro for the symphony that is every physiological system in the human body. And its role is to keep us in balance, to keep us healthy. So, a perfectly functioning and in tune endocannabinoid system keeps us in perfect health”.
https://www.projectcbd.org/medicine/endocannabinology-dr-rachel-knox
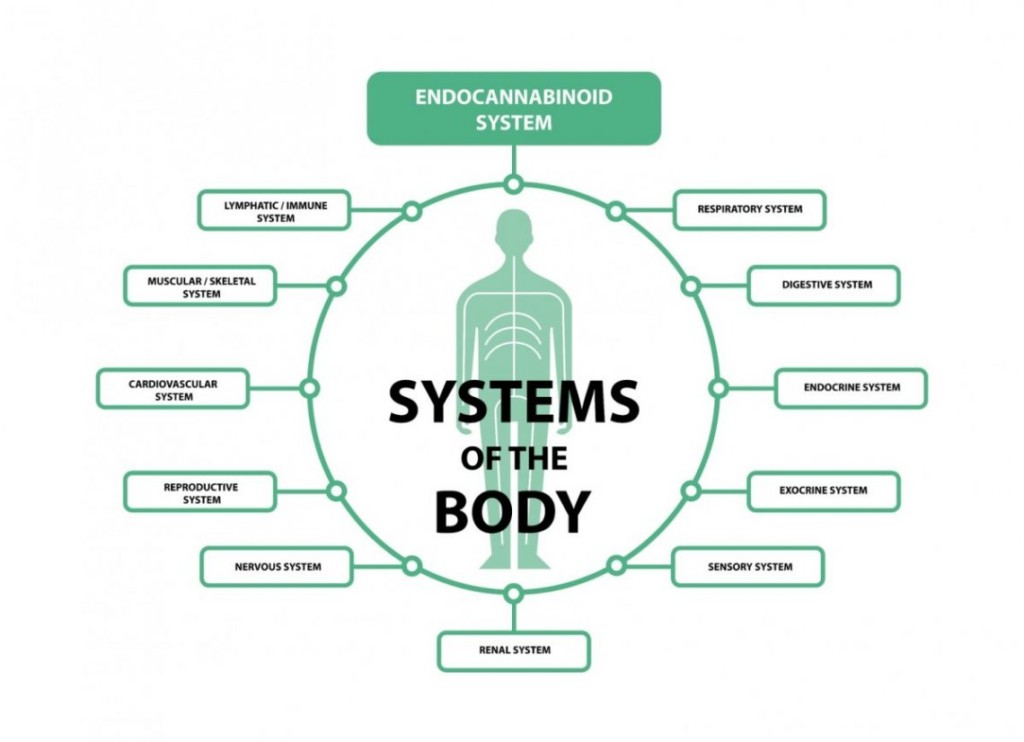
3 Components of the Endocannabinoid System:
- Endocannabinoids (“internal cannabis”). Our bodies are able to synthesize two different cannabinoids, Anandamide and 2-AG. Interestingly, the molecular structure of Anandamide closely resembles THC and the molecular structure of 2-AG is very similar to CBD (our body actually makes its own THC and CBD to control all of our physiologic systems, enhancing our capability of self repair/prevention). These are produced on demand whenever there is an imbalance in the body, such as illness, inflammation, stress or injury. They activate the ECS , which will then take action to help restore our internal environment back to balance.
- Cannabinoid Receptors. These receptors sit on the membranes of cells. The brain has mostly CB1 receptors and they are located in areas of the brain to control pain, memory, emotion, motor control, nausea, appetite and proper intestinal tract function. CB2 receptors are found predominately in the membranes of cells of the immune, lymphatic and peripheral nervous systems.
***Cannabinoids are like “keys” that bind to the “locks” of the CB1 and CB2 receptors activating chemical reaction within the cells.*** - Enzymes. These exist to create Endocannabinoids on demand and also to break them down when they are no longer needed.
Endocannabinoid Deficiency and Cannabis:
The Endocannabinoid System can be overwhelmed by the constant signals caused by Stress, Pain and Inflammation. These signals overload our ECS making it difficult for the body to produce adequate amounts of Endocannabinoids.
Research has demonstrated that Endocannabinoid deficiency plays a role in…
- Autoimmune diseases
- PTSD
- Glaucoma
- Epilepsy/Seizures
- Complex regional pain syndrome/Reflex Sympathetic Dystrophy (the older term)
- Cardiovascular disease
- Depression
- Anxiety
- Migraine
- Chronic Daily Headache
- Irritable Bowel Syndrome
- Schizophrenia
- Bipolar Disorder
- Multiple sclerosis
- Nausea
- Huntington’s disease
- Parkinson’s disease
- Menstrual symptoms
- Treatment-resistant Syndromes
- Phantom Limb Pain
- Motion Sickness
- Cystic Fibrosis
The cannabis plant produces over 130 phytocannabinoids, including tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) and cannabidiol (CBD). These compounds, along with Terpenes and Flavonoids, activate the ECS to restore homeostasis.
- THC mimics the function of our endogenous cannabinoid, Anandamide. Many health conditions have been associated with low levels of Anandamide. Supplementing with THC can function like Anandamide by activating the ECS.
- CBD blocks the breakdown of Anandamide, which helps to increase its levels in the blood. CBD also works on over 65 other receptors and enzyme targets to activate the ECS.
- THC and CBD work synergistically, meaning the combined affect is greater than the sum of their separate effects.
Cannabimimetics:
This refers to non-cannabis plants that activate the ECS or even boost production of Anandamide and 2AG!
For example, Quercetin (found in marigolds and other fruiting plants) can increase our CB1 receptors. Resveratrol, is an antioxidant found in red grapes, peanuts and other plants. It has been found to increase the expression of CB1 and CB2 receptors on the surface of our cells.
Some plants, like soy and aloe can enhance Endocannabinoid system function by delaying the degradation of anandamide.
Activation of CB2 receptors reduces inflammation and helps control obesity, neurodegeneration, autoimmune disorders and arthritis. Celastrol, Echinacea and Magnolia bark activate these receptors. https://www.projectcbd.org/science/other-plants-work-like-cannabis
Diet, Lifestyle and the Endocannabinoid System.
If you want to maximize your response to medical cannabis it would be in your best interest to reduce your intake of carbohydrates, alcohol, sugar and high fructose corn syrup. There is a powerful relationship between the ECS and the Gut-Brain connection. Our typical Western diet is over-starched, over-sweetened and over-processed. This diet is even more harmful in people who are not exercising regularly. Not taking the best possible care of ourselves contributes to the impairment of our ECS.
Scientific evidence clearly supports incorporating more of a plant-based diet and reducing intake of red meat. Taking a probiotic has also been found useful in creating a healthier gut biome, which augments function of the ECS via the Gut-Brain connection.
Beta-caryophyllene (BCP), for example, is a seemingly ubiquitous aromatic terpene present in many spices (black pepper, cloves, rosemary, etc.) and bitter greens, as well as in numerous cannabis varietals. This versatile plant compound conveys significant health benefits by directly activating the CB2 receptor and via other molecular pathways. BCP has been shown to stimulate insulin production and inhibit tumor growth in human cell lines. Mounting evidence suggests that a steady diet of BCP-rich foods could prevent non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Eating green leafy vegetables and spices rich in essential oils may counteract metabolic stress induced by excessive carbohydrate intake.
Healthy fats are also important. Omega 3 polyunsaturated fatty acids, like DHA and EPA are not produced by our body in adequate amounts and must be ingested. The health benefits of omega-3 PUFAs, which are prevalent in oily fish, walnuts, flax and hempseeds, include the prevention of heart disease, dementia, cancer cell proliferation, insulin resistance, and depression.
https://www.projectcbd.org/food-for-thought-diet-cannabis-and-the-endocannabinoid-system
Strive for a high Omega-3, low carb diet with plenty of fresh veggies and spices in addition to cardio exercise for at least 150 minutes weekly.
This article is intended to help you get the most out of treatment with medical cannabis. Good health is hard work, but it sure is worth it.
Updated by Charlie Booras, MD on July 7, 2022