Alzheimer’s Disease and Medical Marijuana (Cannabis)
Alzheimer’s disease is one of the core certifying conditions qualifying a client for treatment with Medical Cannabis. This means that scientific evidence has shown clear benefits from cannabis therapy.
Description: Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is a chronic, progressive neurodegenerative disease causing 60–70% of cases of dementia. Typical symptoms include difficulty in remembering recent events, problems with language, disorientation (including easily getting lost), mood swings, loss of motivation, not managing self-care, and behavioral issues.
The cause is poorly understood but a common finding is the presence of “amyloid plaque” and “neurofibrillary tangles” in the brain during special imaging or at autopsy. At this time, a definitive cause has not been established.
Risk factors include a family history of AD, head injuries, depression and cardiovascular risk factors (especially Hypertension). It has been shown that a sedentary lifestyle increases risk. Most cases develop after age 65.
Conventional treatment: “No medication has been clearly shown to delay or halt progression of the disease”. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Alzheimer’s_disease
Acetylcholinesterase Inhibitors. There are several medications in this family, all of which strive to reduce the rate at which acetylcholine is broken down in brain tissue. Multiple studies have shown that “benefit from their use is small”.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Alzheimer’s_disease#cite_note-pmid16437532-178
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Alzheimer’s_disease#cite_note-Birks2015-174
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Alzheimer’s_disease#cite_note-175
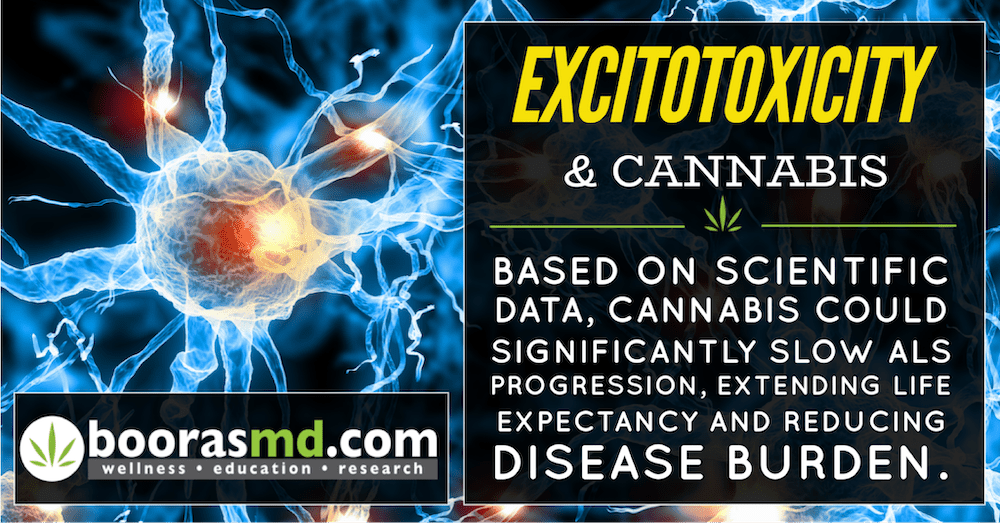
NMDA Receptor Antagonist. The only drug in this class is Namenda (memantine). It acts on the glutamatergic system to inhibit overstimulation of nerves by glutamate, an excitatory neurotransmitter in the brain. Too much glutamate causes death of nerve cells through a process called Excitotoxicity, which occurs in AD, Parkinson’s disease, ALS and Multiple Sclerosis. Memantine alone provides a small benefit in moderate to severe AD, but combining it with donepazil (one of the acetylcholinesterase inhibitors) has been shown to be of “statistically significant but clinically marginal effectiveness”.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Alzheimer’s_disease#cite_note-pmid18316756-185
Medical Cannabis: “Finding a therapy for Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is perhaps the greatest challenge for modern medicine”. https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s12035-019-1637-8
Testing has shown that THC and CBD have neuroprotective activity in addition to preventing oxidant-induced cell death. They also have been shown to remove beta-Amyloid plaque and reduce glutamate toxicity (Excitotoxicty). Testing on cell lines that do not have CB1 or CB2 receptors “suggest that these cannabinoids work through a number of mechanisms beyond just the Endocannabinoid system”.
https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s12035-019-1637-8
References:
https://www.karger.com/Article/Abstract/498924
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5766723/
Written by Charlie Booras, MD on 8/16/20